Engineering Geology for the Snowy Mountains Scheme
These data, considered in conjunction with the core and the drillers’ observations, enable a better and more comprehensive assessment to be made of the soundness and permeability of the rock than can be made on the basis of cores (usually incomplete) alone. Costs of these additional tests are only a small addition to the cost of drilling for core alone.
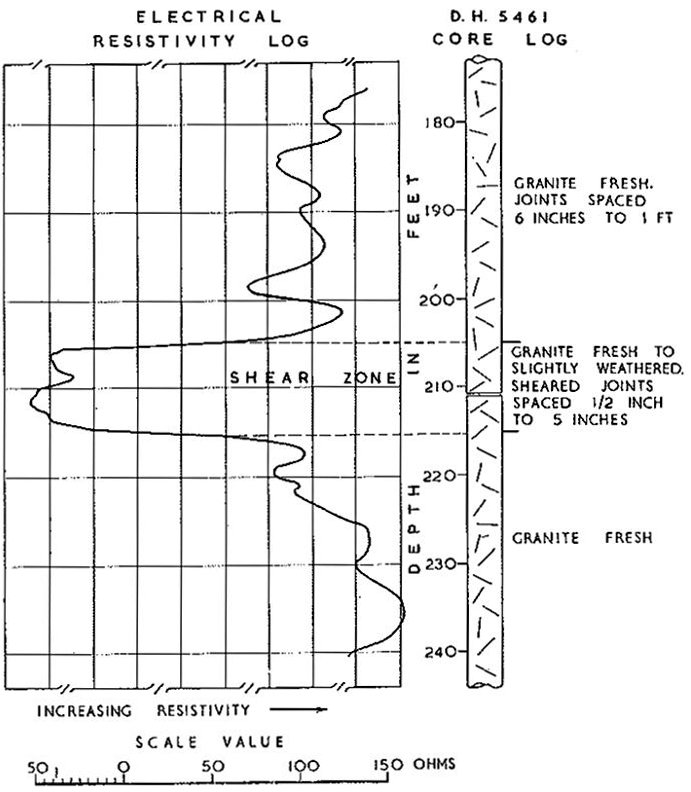
Fig. 7.—Electrical Resisivity Log of Part of a Diamond Drill Hole
Seismic Refraction Surveys:
The seismic refraction method has been applied on a considerable number of investigations, and to a variety of problems. This geophysical method of exploration has been used fairly widely on engineering investigations, particularly in the United States (Ref 5) and in Sweden. In the Snowy Mountains area, the first investigations were made for the Authority by geophysicists of the Commonwealth Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics, at the Kosciusko Dam site at Spencer’s Creek. Subsequently, the Authority established its own geophysical unit.
The equipment used in the Snowy Mountains investigations is a 12-channel refraction seismograph.
In this method a seismic line or “spread” is laid out as a straight line on the ground, and 12 geophones or seismic wave detectors are set out at measured intervals thereon. Following this a small explosive charge is buried in the ground near the end of the spread and detonated. This position is known as the “shot point”. Similar charges are later detonated near the other end of the spread.
The time of travel of the seismic waves or vibrations from the shot point through the ground to each of the geophones along the spread is measured and photographically recorded. From these records or seismograms, obtained on each spread, a travel-time graph is plotted.
