Rock mechanics in the investigation and construction of Tumut 1 Underground Power Station, Snowy Mountains, Australia
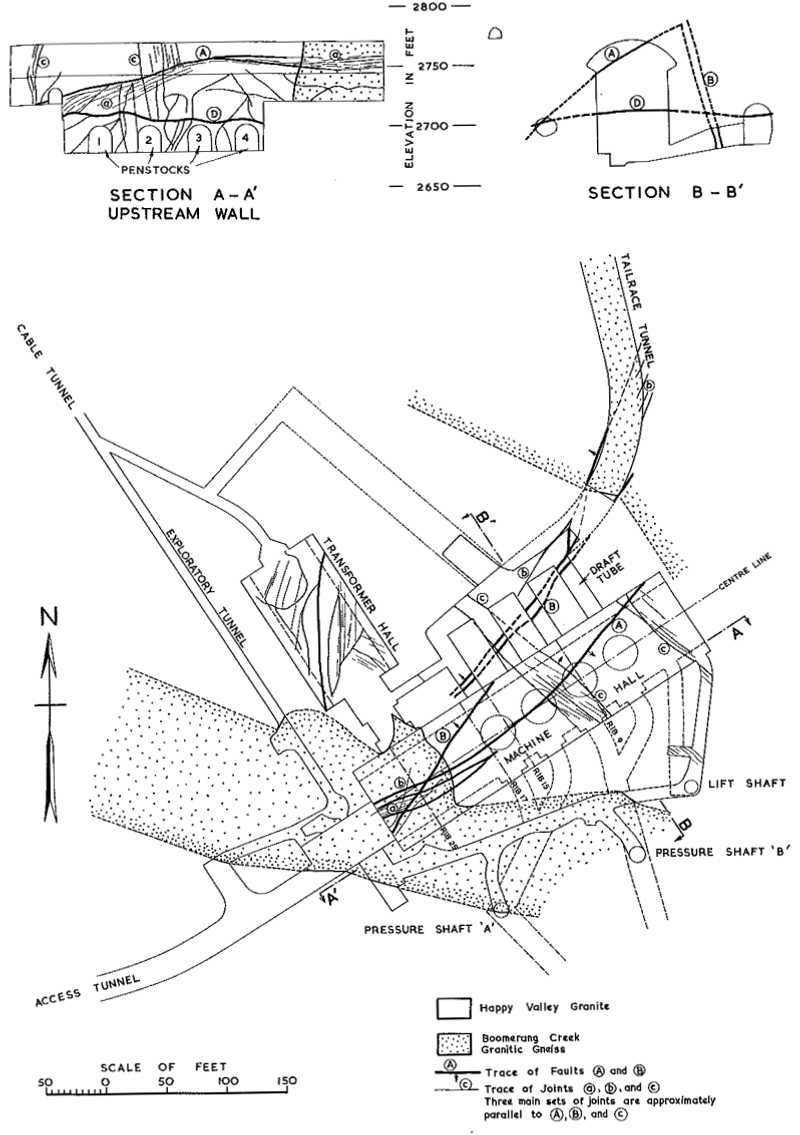
Figure 4 – Plan and Sections of the Power Station
Fault A is quite similar in attitude to the surge-tank fault and the other major overthrust faults and is considered to be contemporaneous with them. lt also is probably an overthrust fault, of very small displacement, and the joints of set a are shear joints parallel to this fault.
These structures could have been caused by a system of stress with maximum compression in the northwest-southeast direction, in which case the joints of set c parallel to this direction are interpreted as tension fractures developed at the same time. The last movement along fault B indicated by the slickensides was nearly parallel to the dip. The joints of set b appear to be shear joints. Fracture zone D has many characteristics of a tension fracture.
The major overthrust faults intersect some basalt dikes of probably early Tertiary age. This faulting was probably accompanied by small movement on many joints and the development of the minor faults at the power-station site. No doubt the rock mass was extensively jointed previously, and thus much of the latest movement occurred along these existing joints. Many of the joints of the granite in particular look as though they were originally rough tension fractures, along which slight shearing movements later planed off some but not all the interlocking rough points.
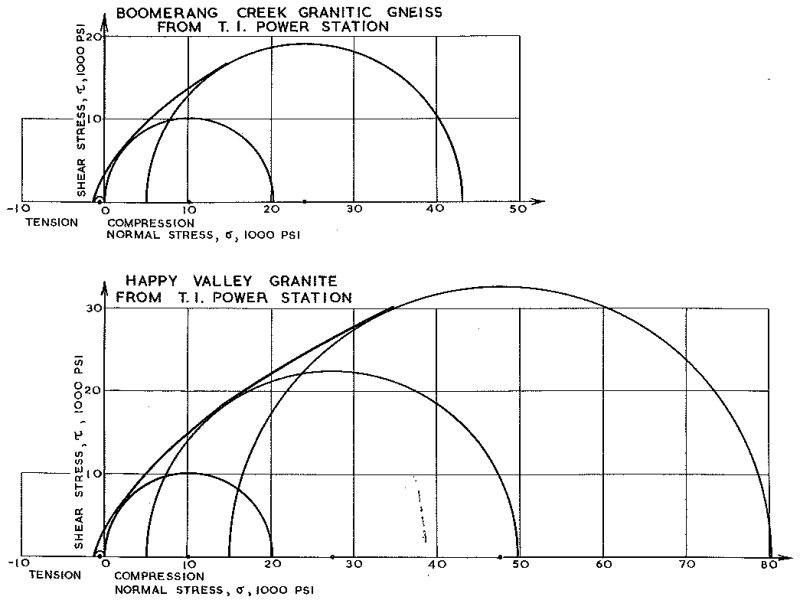
Figure 5 – Mohr Envelopes
