Rock mechanics in the investigation and construction of Tumut 1 Underground Power Station, Snowy Mountains, Australia
Happy Valley Granite
In hand specimen the granite is a granular, medium-grained rock, light gray, without distinct foliation or preferred orientation of minerals. Grains of gray glassy quartz, white or greenish-white feldspar, and flakes of black biotite can be recognised readily by the unaided eye.
Under the microscope it is entirely crystalline, the grain size is rather variable and ranges from 0.3 to 1.5 mm in diameter; occasional plagioclase grains are up to 4 mm in diameter. The grain boundaries usually are interlocking. Also, in hand specimens, the granite appears to be rather variable in composition. The quantitative mineralogical composition determined on five to nine thin sections from each of three representative samples is given in Table 2.
Much of the biotite is considerably chloritized, for example in sample 3, especially in narrow zones close to joints. Minor constituents are zircon and apatite. Cordierite does not occur.
From its field relationships, Happy Valley granite is considered to be an intrusive igneous rock, which petrologically may be classified as tonalite.
Strength and Elastic Properties
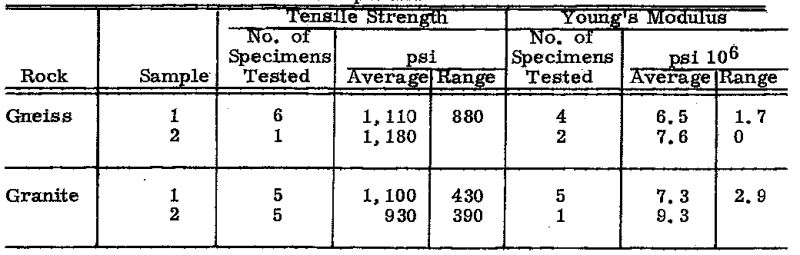
The strength and elastic properties of the rocks were measured on pieces of drill cores free from visible joints or other defects. The cores were 1 ⅞ or 2 inches in diameter, and the lengths of the test pieces were twice their diameters. The results of the tests are summarized by showing the number of specimens tested, the average value of the results, and the range. The sample numbers in Tables 3–6 refer to the same samples as in Tables 1–2.
The relatively low strength of granite sample 3 and the wide scatter of the test results appear related to the fact that the biotite in the sample was very extensively but variable altered to chlorite.
TABLE 2
Happy Valley Granite (Tonalite)
(Analyst: D. Lafeber)
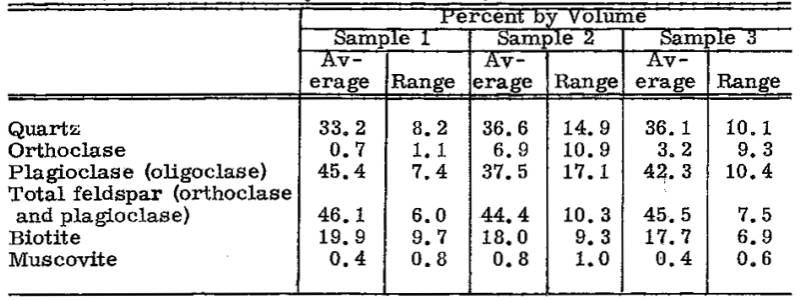
TABLE 3
Compressive Properties
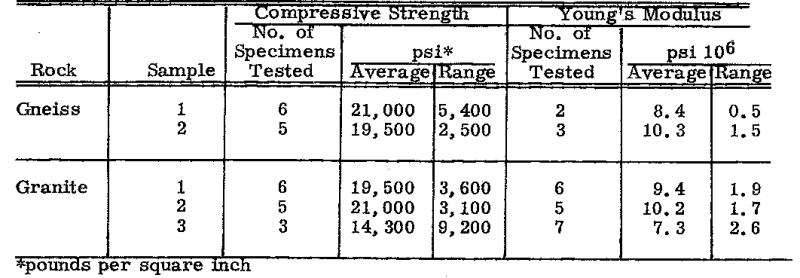
TABLE 4
Tensile Properties