Discussion at Technical Session No. 9—Rock Mechanics
References
1. U.S. Bureau of Reclamation (1939)—Boulder Canyon Project, Final Report, Part V.—Technical Investigations, Bulletin 4, pp. 267-268.
2. Talobre, J. (1957)—La Mechanique des Roches (Dunod: Paris), p. 58.
3. Timoshenko S. and Goodier, G. N. (1951)—Theory of Elasticity. 2nd Edit. p. 201 (McGraw-Hill; New York).
Professor J. C. Jaeger:
—(Written contribution submitted after the Conference.)
The writer had the privilege of seeing some of the early work of the Snowy Mountains Authority when what were then regarded as anomalously high horizontal stresses were measured underground. Because of the difficulty of making comprehensive measurements underground it seemed worth while trying to study the behaviour of rocks containing flat jacks in the laboratory. Actual underground experiments are made on carefully selected rocks, regarded as sound, which are, by inference, immersed in less sound or more closely jointed rock. Three questions then arise which can be attacked in the laboratory: (i) how far do jack pressures correspond with stresses in sound rock, (ii) how does unsound rock behave under the same conditions, and (iii) what is the effect of irregular loading? In connection with the latter point, it should be said that the individual rock on which measurements are made is stressed across joints by other portions of the rock mass, and when an excavation is opened up this distribution of stresses will change so that the stress in the rock may well be highly inhomogeneous.
To see how far these matters could be studied in the laboratory, a standard S.M.A. jack, 1 foot square, was set in a block of 1:2:4 concrete 2 ft. × 2 ft. 6 in. × 1 ft. 7 in. and loaded below a spherical seat in a testing machine.
This size was chosen partly because of the platen size, and partly to give about 6 in. clearance around the jack. This block and another gave highly anomalous results which will be described later; in view of these, and difficulties due to creep in the concrete, it was decided to experiment on blocks of solid, sound rock.
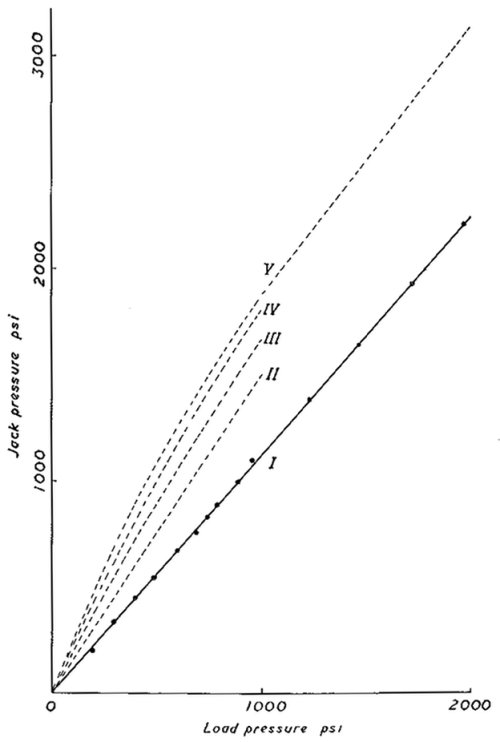
Fig. 9b. —The Relationship between Load Stress in a Block and the
Jack Pressure Necessary to make the Displacement Approximateiy
the Same at All Measuring Points.
Curve 1 for marble, dots are experimental points. curves 11-V for concrete
blocks with internal cracks.
